Tight transmission bottlenecks may limit the evolution of SARS-CoV-2 variants NaturePortfolio UMich TransmissionBottleneck Variant SARSCoV2 COVID19 VariantsofConcern
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D.Jan 18 2023Reviewed by Aimee Molineux A study published in Nature Communications describes that tight transmission bottlenecks restrict the evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in the transmission chain. SARS-CoV-2 is the causative pathogen of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
Therefore, tight transmission bottlenecks restrict the adaptive evolution of a virus by preventing the onward spread of newly accumulated mutations. Tight transmission bottlenecks have previously been observed for many viruses, including human immunodeficiency virus , influenza virus, and SARS-CoV-2.
Genetics & Genomics eBook Compilation of the top interviews, articles, and news in the last year. Download a free copy Based on the sequencing results, the final transmission analysis included 45 households, 110 individuals, and 134 possible transmission pairs. The SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern identified in these households were alpha, beta, delta, and omicron.
Transmission bottleneck The genetic diversity shared between the household members of a transmission pair was used to calculate the transmission bottleneck. Within a household, a transmission pair includes the index case as the donor and the contact as the recipient.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
Haemorrhage of human foetal cortex associated with SARS-CoV-2 infectionMassimo et al. report the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in first and second trimester foetal brain tissue in association with cortical haemorrhages. The haemorrhages w
続きを読む »
 Overall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescentsOverall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescents medrxivpreprint UniBasel_en unibern institutpasteur sheffielduni SARSCoV2 covid coronavirus covid variantsofconcern childhealth teenagers
Overall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescentsOverall patterns of SARS-CoV-2 caused by variants of concern among children and adolescents medrxivpreprint UniBasel_en unibern institutpasteur sheffielduni SARSCoV2 covid coronavirus covid variantsofconcern childhealth teenagers
続きを読む »
 The 'Great Escape' by SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1In a recent article published in the Lancet Microbe, researchers in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom quantified the antigenic diversity of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) subvariants, BQ.1.1, BM.1.1.1, and XBB.1, all derivatives of the variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, which emerged in late 2022.
The 'Great Escape' by SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1In a recent article published in the Lancet Microbe, researchers in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom quantified the antigenic diversity of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) subvariants, BQ.1.1, BM.1.1.1, and XBB.1, all derivatives of the variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, which emerged in late 2022.
続きを読む »
 S. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein AS. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein A WesternU SARSCoV2 bacteria virus covid coronavirus covid
S. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein AS. aureus enhances replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro through the bacterial iron-regulated surface determinant protein A WesternU SARSCoV2 bacteria virus covid coronavirus covid
続きを読む »
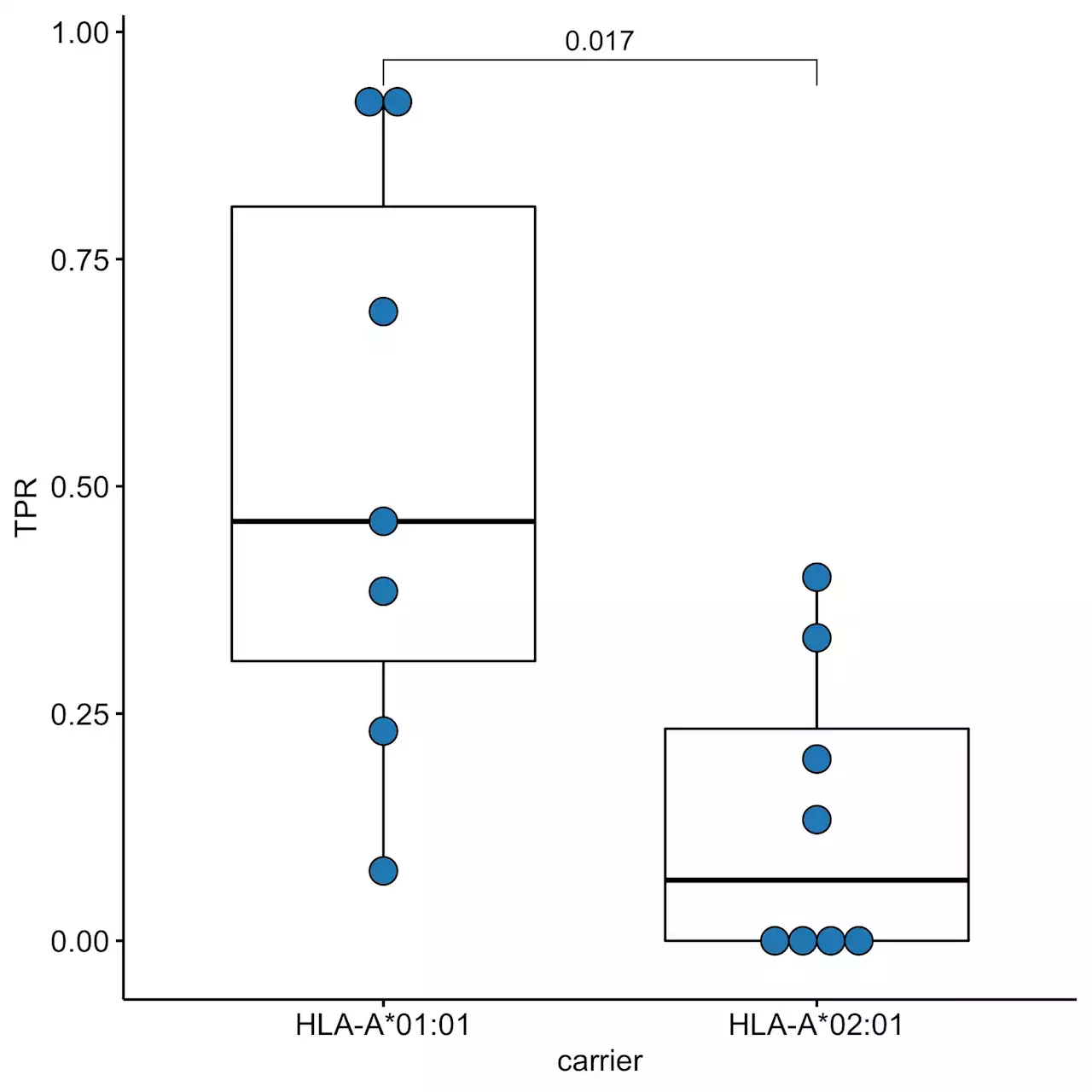 Researchers reveal genetic predisposition to immunity against new variants of COVID-19The SARS-CoV-2 delta variant that caused the third wave of COVID-19 in mid-2021 turned out to be more contagious than earlier SARS-CoV-2 variants. In addition, protein mutations in the delta variant were found to significantly reduce the effect of acquired humoral immunity to COVID-19 from prior infection or vaccination.
Researchers reveal genetic predisposition to immunity against new variants of COVID-19The SARS-CoV-2 delta variant that caused the third wave of COVID-19 in mid-2021 turned out to be more contagious than earlier SARS-CoV-2 variants. In addition, protein mutations in the delta variant were found to significantly reduce the effect of acquired humoral immunity to COVID-19 from prior infection or vaccination.
続きを読む »