When Yale neuroscientist Joy Hirsch used sophisticated imaging tools to track in real time the brain activity of two people engaged in conversation, she discovered an intricate choreography of neural activity in areas of the brain that govern social interactions.
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use ourThank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
 Lung cancer cells covertly thrive in brain under guise of protection, study findsLung cancer cells that metastasize to the brain survive by convincing brain cells called astrocytes that they are baby neurons in need of protection, according to a study by researchers at Stanford Medicine.
Lung cancer cells covertly thrive in brain under guise of protection, study findsLung cancer cells that metastasize to the brain survive by convincing brain cells called astrocytes that they are baby neurons in need of protection, according to a study by researchers at Stanford Medicine.
続きを読む »
 Brain clues in the battle against long COVID: study pinpoints neuroinflammationThe relationship between circulating markers of vascular dysfunction and neuroinflammation.
Brain clues in the battle against long COVID: study pinpoints neuroinflammationThe relationship between circulating markers of vascular dysfunction and neuroinflammation.
続きを読む »
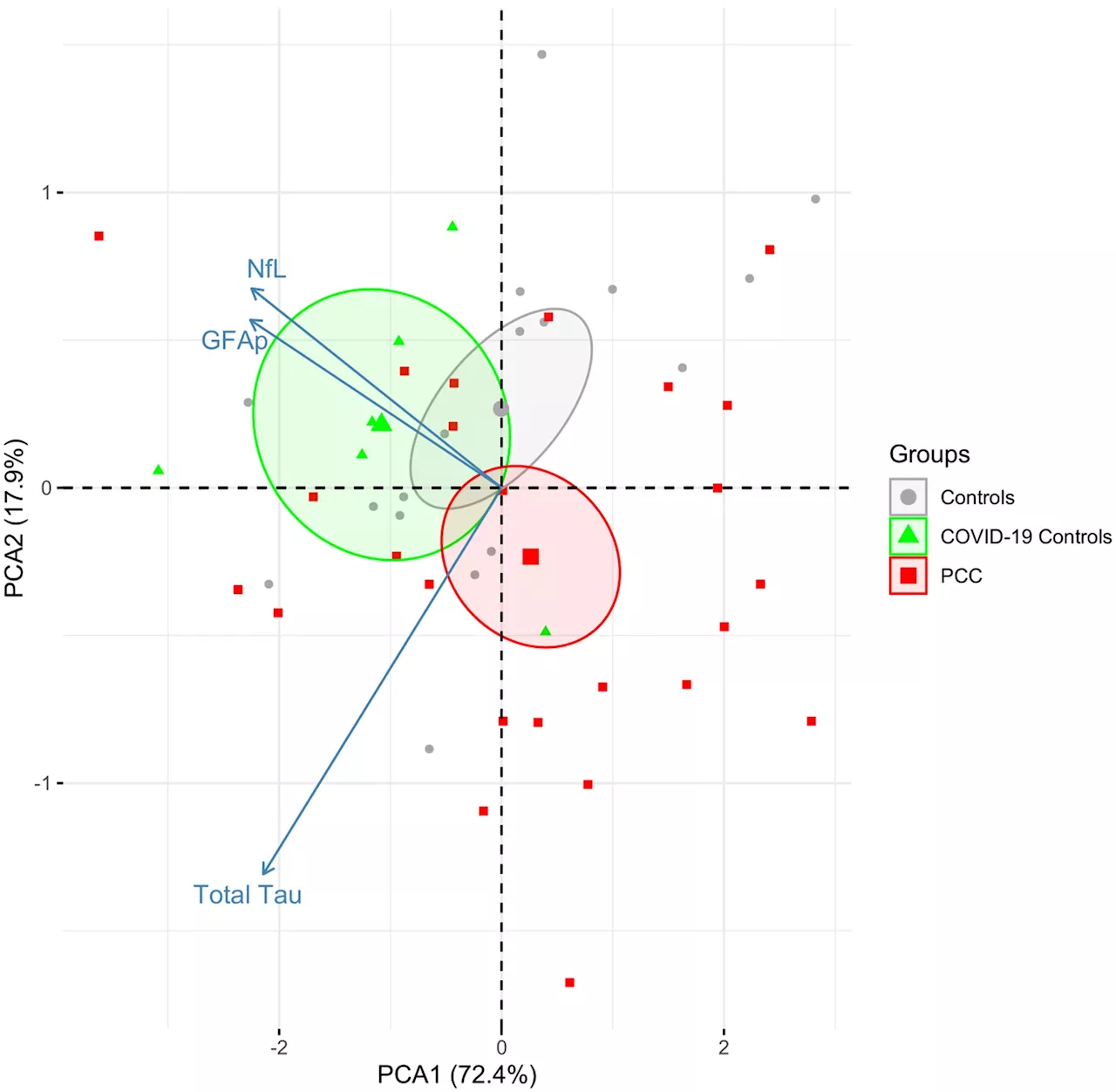 Post-COVID condition is not linked to ongoing infection or active brain damage, study showsPost COVID-19 condition does not appear to be linked to direct viral invasion of the brain or active brain damage. This has been shown in a study by researchers at the University of Gothenburg. Searching for abnormal biomarkers among the participants yielded no hits in either blood or cerebrospinal fluid samples.
Post-COVID condition is not linked to ongoing infection or active brain damage, study showsPost COVID-19 condition does not appear to be linked to direct viral invasion of the brain or active brain damage. This has been shown in a study by researchers at the University of Gothenburg. Searching for abnormal biomarkers among the participants yielded no hits in either blood or cerebrospinal fluid samples.
続きを読む »
 Study suggests marijuana use damages brain immune cells vital to adolescent developmentIn a mouse study designed to explore the impact of marijuana's major psychoactive compound, THC, on teenage brains, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found changes to the structure of microglia, which are specialized brain immune cells, that may worsen a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia.
Study suggests marijuana use damages brain immune cells vital to adolescent developmentIn a mouse study designed to explore the impact of marijuana's major psychoactive compound, THC, on teenage brains, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found changes to the structure of microglia, which are specialized brain immune cells, that may worsen a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia.
続きを読む »
 Study sheds light on how cocaine addiction alters brain's reward systemRutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain's system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel.
Study sheds light on how cocaine addiction alters brain's reward systemRutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain's system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel.
続きを読む »
 Study reveals an alternate origin of brain mosaicism in some children with focal epilepsyIn most people, every cell in their body contains the same genetic information. However, sometimes people can have two or more genetically different sets of cells.
Study reveals an alternate origin of brain mosaicism in some children with focal epilepsyIn most people, every cell in their body contains the same genetic information. However, sometimes people can have two or more genetically different sets of cells.
続きを読む »
