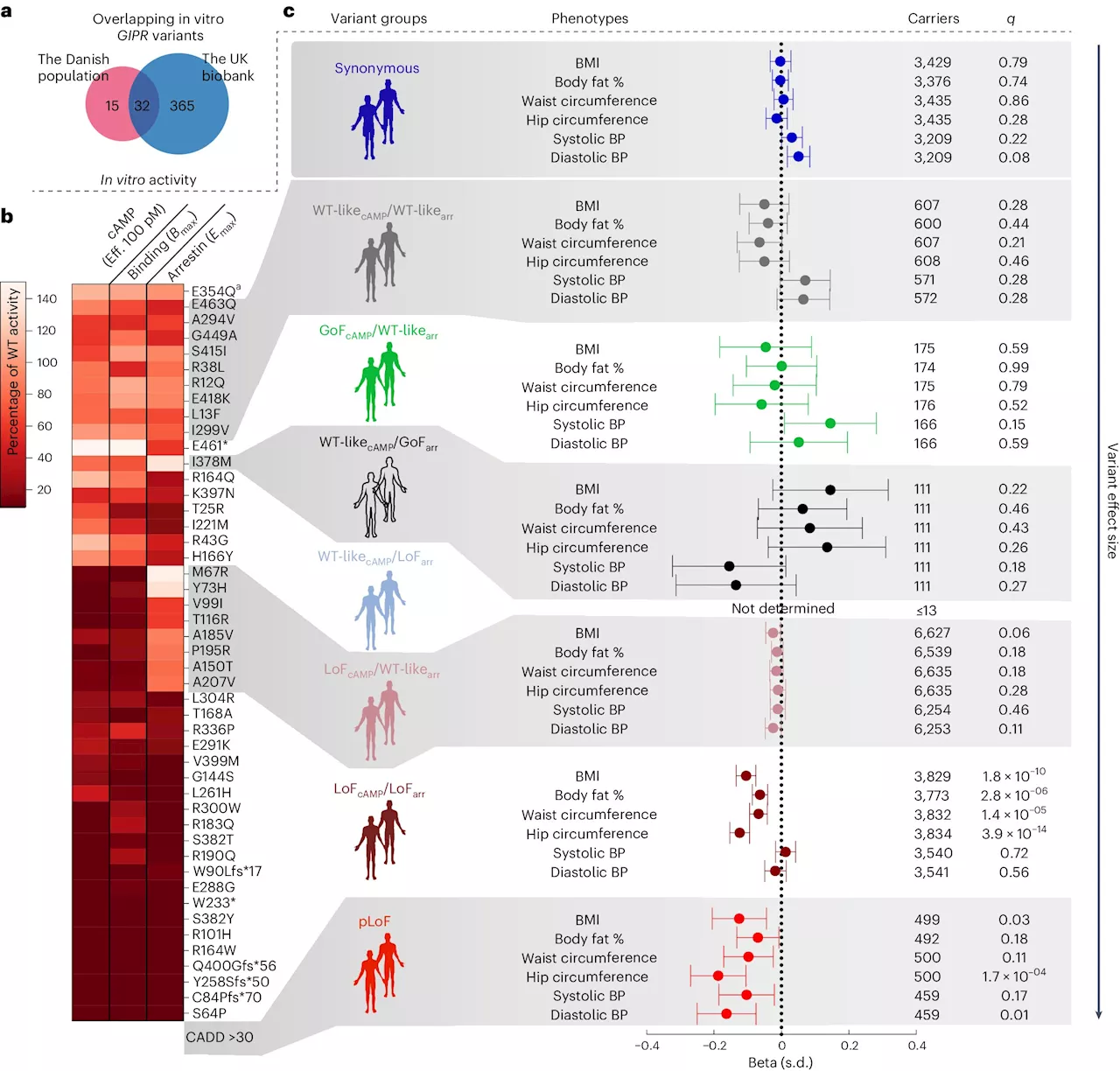
Researchers reviewed studies on dietary impacts of GLP-1 and GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonists in obesity and T2D patients, finding significant caloric reduction but limited evaluation of dietary composition.
By Hugo Francisco de SouzaReviewed by Susha Cheriyedath, M.Sc.Jul 29 2024 In a recent review published in the journal Obesity Pillars, a team of researchers collate and narratively review the literature on the dietary impacts of obesity or type 2 diabetes patients undergoing glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists or glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists clinical interventions.
Background Obesity, clinically defined as a body mass index over 35 kg/m2, is an alarming public health condition. The World Health Organization estimates that 16% of the global adult population suffers from the condition, with this prevalence highest in developed countries such as the United States .
About the study The present narrative review aims to elucidate the role of GLP-1 or GIP/GLP-1 RA interventions on the dietary intake of obesity or T2D patients. Specifically, the authors investigated In interventions involving RA versus placebo, dietary intake was reduced by between 16% and 39% in the former cohort. In contrast, RA versus counseling interventions failed to report statistically significant dietary intake reductions. Notably, only one study employed the ‘gold standard’ of dietary intake measurement – the 24-hour dietary recall. The other studies employed variations of a standardized test meal to evaluate dietary intake.
GLP-1 Semaglutide Weight Loss Agonist Diabetes Drugs Food Glucagon Glucose Minerals Obesity Protein Receptor Research Type 2 Diabetes Vitamins
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
 Sister hormone of GLP-1 could lead to better weight-loss drugsMuch like the Cold War space race, the world's pharmaceutical giants are currently scrambling to produce the best weight-loss drug. They all want to be the first to explore the nooks and crannies of the body in order to be able to design the optimal drug. However, several pharmaceutical giants disagree on what the next step should be.
Sister hormone of GLP-1 could lead to better weight-loss drugsMuch like the Cold War space race, the world's pharmaceutical giants are currently scrambling to produce the best weight-loss drug. They all want to be the first to explore the nooks and crannies of the body in order to be able to design the optimal drug. However, several pharmaceutical giants disagree on what the next step should be.
続きを読む »
 GLP-1-based polyagonists: A promising weight loss alternative to bariatric surgeryResearchers highlight the unprecedented success of GLP-1-based multi-receptor drugs in achieving substantial weight loss and improved health outcomes, potentially replacing bariatric surgery for obesity treatment.
GLP-1-based polyagonists: A promising weight loss alternative to bariatric surgeryResearchers highlight the unprecedented success of GLP-1-based multi-receptor drugs in achieving substantial weight loss and improved health outcomes, potentially replacing bariatric surgery for obesity treatment.
続きを読む »
Beyond the anti-obesity benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1 drugsThe advantages of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) medicines beyond glycemic and weight control.
続きを読む »
 Study indicates surge in GLP-1RA prescriptions to treat obesity and prevent its complicationsInvestigators at Cedars-Sinai and other institutions conducted a nationwide, population-based study to identify trends in the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs)—prescription medications sold under popular drug names like Ozempic and Wegovy—in the United States.
Study indicates surge in GLP-1RA prescriptions to treat obesity and prevent its complicationsInvestigators at Cedars-Sinai and other institutions conducted a nationwide, population-based study to identify trends in the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs)—prescription medications sold under popular drug names like Ozempic and Wegovy—in the United States.
続きを読む »
 Exploring the expanding horizons of GLP-1 therapies beyond diabetes and obesityIn a Perspective, Daniel Drucker highlights the growing body of evidence that hints at the potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-based medications in treating conditions other than diabetes and obesity, including cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative disorders.
Exploring the expanding horizons of GLP-1 therapies beyond diabetes and obesityIn a Perspective, Daniel Drucker highlights the growing body of evidence that hints at the potential of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)-based medications in treating conditions other than diabetes and obesity, including cardiovascular disease and neurodegenerative disorders.
続きを読む »
 GLP-1 drugs found to lower cancer risk in diabetes patientsResearch finds that GLP-1 receptor agonists significantly reduce the risk of 10 out of 13 obesity-associated cancers in type 2 diabetes patients compared to insulins, but show varied results against metformin.
GLP-1 drugs found to lower cancer risk in diabetes patientsResearch finds that GLP-1 receptor agonists significantly reduce the risk of 10 out of 13 obesity-associated cancers in type 2 diabetes patients compared to insulins, but show varied results against metformin.
続きを読む »
