Researchers believe there may be a way to target ‘sleeping’ breast cancer cells and prevent relapse.
Scientists have discovered how breast cancer cells can evade treatment by “hibernating” and then “wake up” years later – causing a relapse that is more difficult to treat.
Luca Magnani, professor of epigenetic plasticity at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, said: “After surgery to remove primary oestrogen receptor positive breast cancer, patients are given five to 10 years of hormone therapy which aims to kill any remaining cancer cells. “Our research identified a key mechanism used by cancer cells to evade therapy by remaining in a dormant state, hibernating before they ‘wake up’ years later and begin to rapidly divide again.
Treatment often involves a combination of different therapies and surgery, usually tailored to the patient’s needs. Dr Tayyaba Jiwani, science engagement manager at Cancer Research UK – which funded the research, said: “Breast cancer survival has doubled in the UK over the last 50 years thanks to better detection and screening, but there are still more than 11,000 deaths from this type of cancer every year.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
Scientists discover how breast cancer cells become dormant and evade treatmentResearchers believe there may be a way to target ‘sleeping’ breast cancer cells and prevent relapse.
続きを読む »
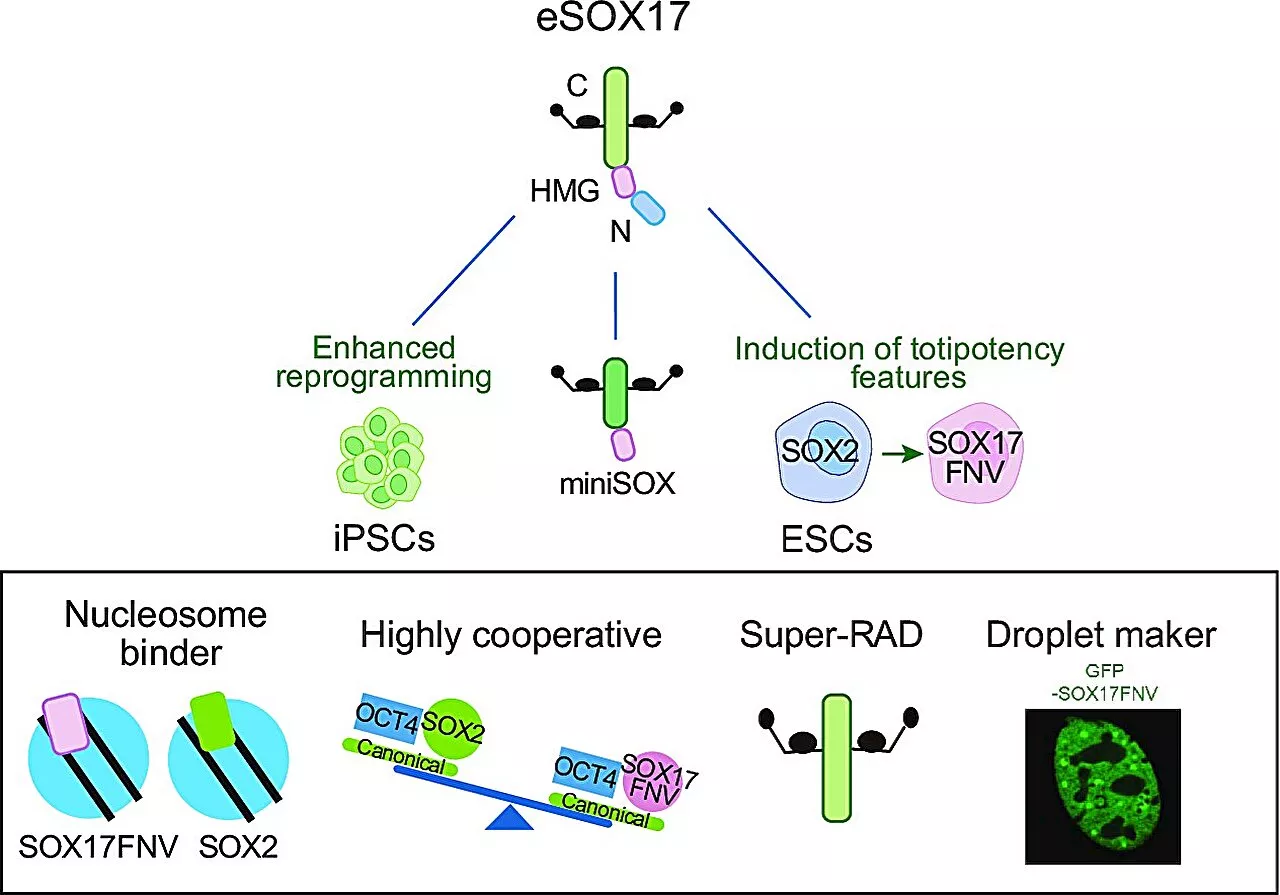 Researchers develop shortcut to generate brain stem cells for age-related disease researchA research team from the School of Biomedical Sciences, LKS Faculty of Medicine of the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), has achieved a breakthrough in stem cell research, offering tools that can be used for patients who require highly personalized care.
Researchers develop shortcut to generate brain stem cells for age-related disease researchA research team from the School of Biomedical Sciences, LKS Faculty of Medicine of the University of Hong Kong (HKUMed), has achieved a breakthrough in stem cell research, offering tools that can be used for patients who require highly personalized care.
続きを読む »
 Our cells are less likely to express longer genes as we age, researchers sayAging may be less about specific 'aging genes' and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece published March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics.
Our cells are less likely to express longer genes as we age, researchers sayAging may be less about specific 'aging genes' and more about how long a gene is. Many of the changes associated with aging could be occurring due to decreased expression of long genes, say researchers in an opinion piece published March 21 in the journal Trends in Genetics.
続きを読む »
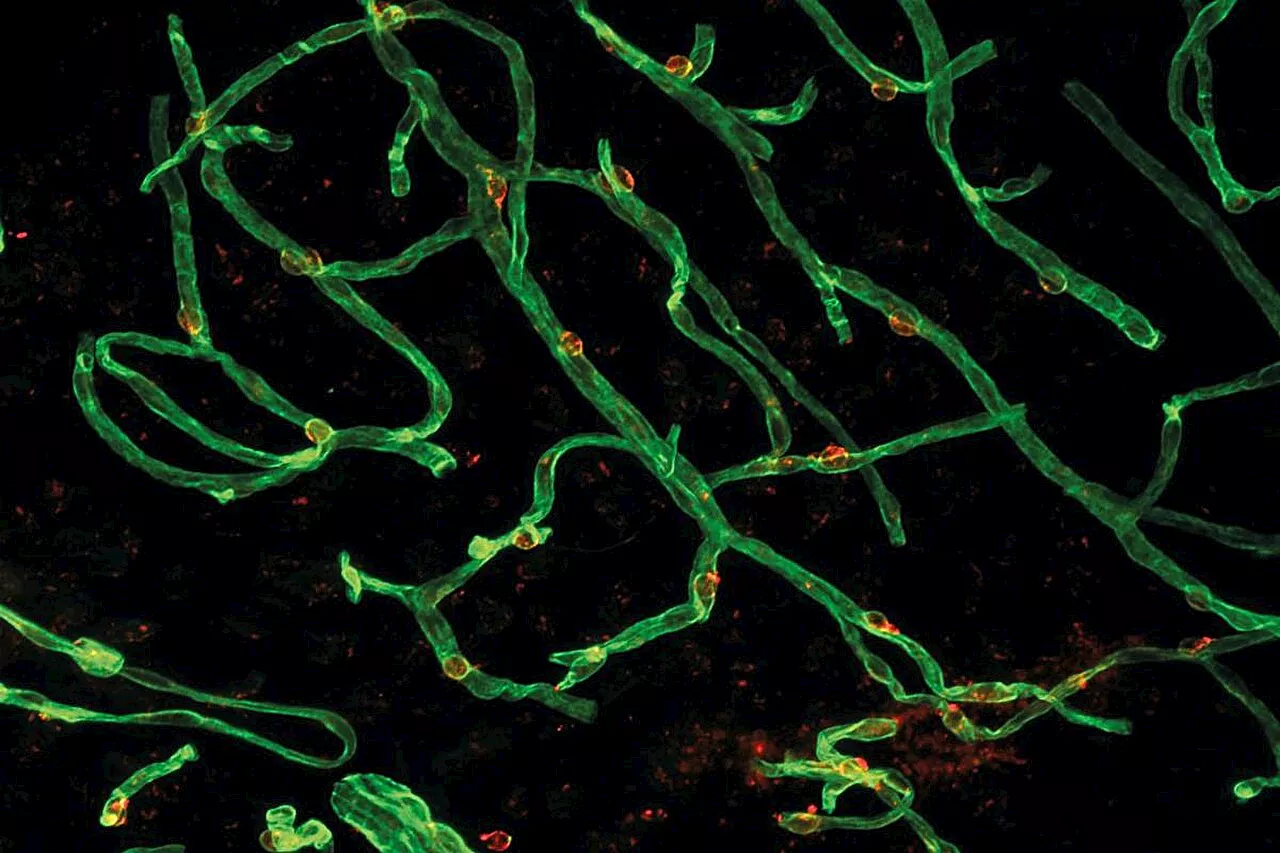 Researchers analyze how the proteome of specific brain cells changes as we ageFor the neurons in the brain to work smoothly and be able to process information, the central nervous system needs a strictly regulated environment.
Researchers analyze how the proteome of specific brain cells changes as we ageFor the neurons in the brain to work smoothly and be able to process information, the central nervous system needs a strictly regulated environment.
続きを読む »
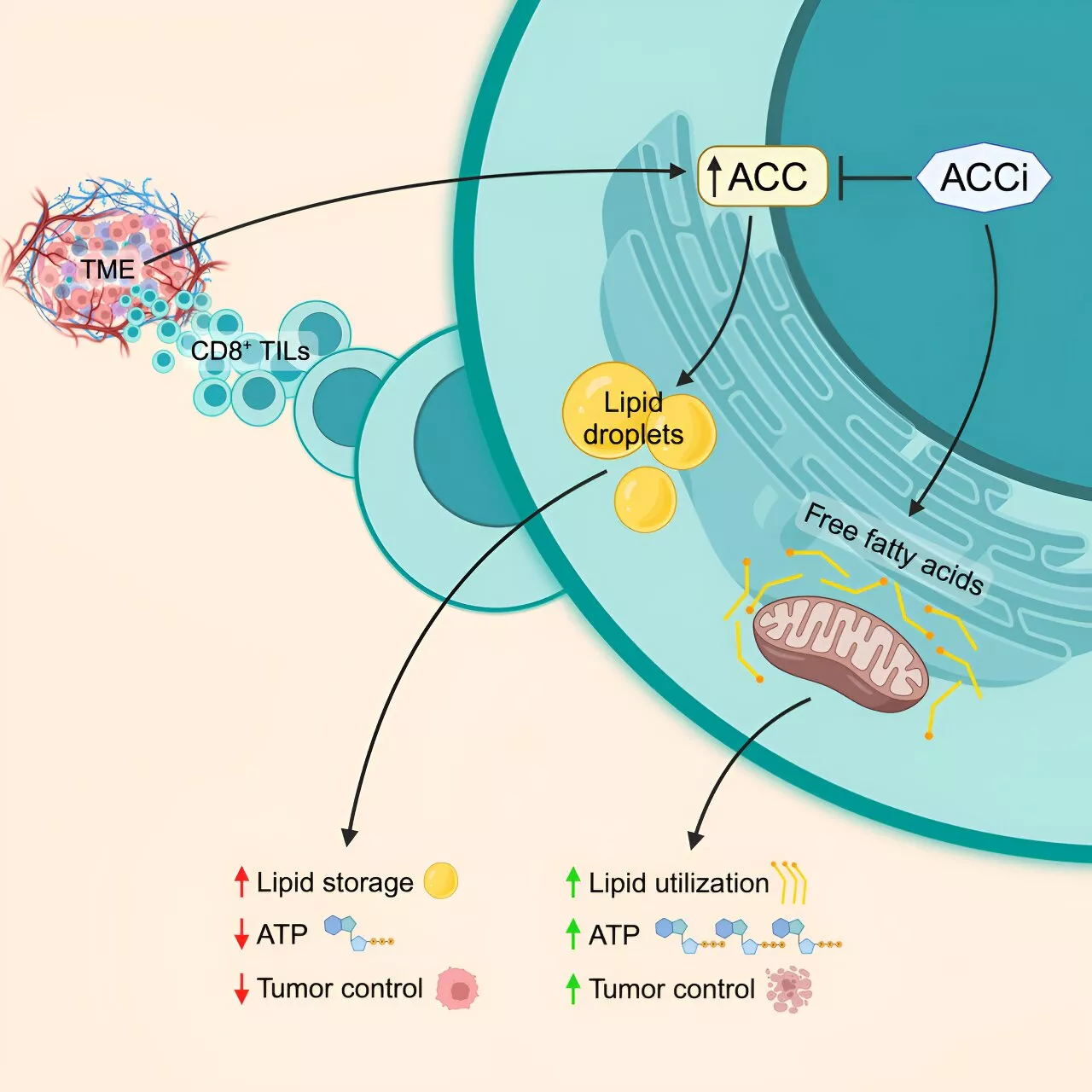 Researchers gain insight into why T cells lose energy in solid tumorsT cells are often called 'assassins' or 'killers' because they can orchestrate and carry out missions to hunt down bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells throughout the body. Mighty as they may be, recent research has shown that once T cells infiltrate the environment of a solid tumor, they lose the energy needed to combat the cancer.
Researchers gain insight into why T cells lose energy in solid tumorsT cells are often called 'assassins' or 'killers' because they can orchestrate and carry out missions to hunt down bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells throughout the body. Mighty as they may be, recent research has shown that once T cells infiltrate the environment of a solid tumor, they lose the energy needed to combat the cancer.
続きを読む »
 Researchers create more realistic synthetic human mini heartsThanks to advancements in the development of patented synthetic human-like hearts first created at Michigan State, researchers can study human heart development and congenital heart disease on highly accurate models.
Researchers create more realistic synthetic human mini heartsThanks to advancements in the development of patented synthetic human-like hearts first created at Michigan State, researchers can study human heart development and congenital heart disease on highly accurate models.
続きを読む »