Complex path promotes immune cell migration and clearance of toxic protein. Reducing the methylation of a key messenger RNA can promote migration of macrophages into the brain and ameliorate symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease in a mouse model, according to a new study published on March 7th in the ope
A study published in PLOS Biology suggests that reducing methylation of a messenger RNA can help in the migration of macrophages to the brain and alleviate Alzheimer’s disease symptoms in a mouse model. This study highlights a potential pathway for immune cells to enter the brain and could provide a new target for Alzheimer’s treatment.
One potential pathway for getting rid of amyloid-beta is the migration of blood-derived myeloid cells into the brain, and their maturation into macrophages, which, along with resident microglia, can consume amyloid-beta. That migration is a complex phenomenon controlled by multiple interacting players, but a potentially important one is the methylation of messenger RNA within the myeloid cells.
How did decreased mRNA methylation promote myeloid cell migration? The authors elucidated a complex mechanism. Through analysis of mRNA expression patterns and other techniques, they showed that depletion of METTL3 reduced the activity of a key m6A reader protein, which recognizes m6A-modified mRNAs and promotes their translation into protein. That led to a decline in another protein, and that inhibited the production of yet another protein, called ATAT1.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
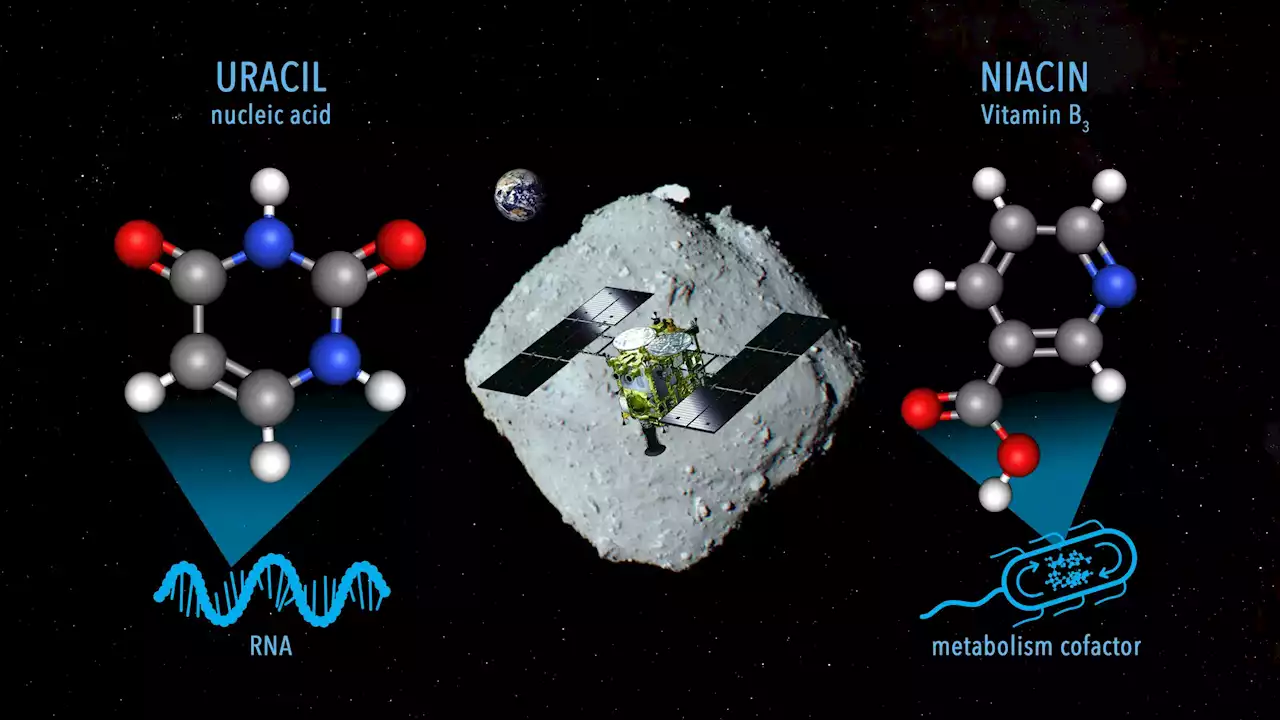 Component of RNA Found in Asteroid Ryugu SamplesSamples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA. Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one
Component of RNA Found in Asteroid Ryugu SamplesSamples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA. Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one
続きを読む »
 Big pharma craves slice of AI-based RNA drug discovery - Nature BiotechnologyIn Brief: In recent months, at least eight companies have been launched to develop RNA-modulating small molecules, and all have signed collaborations with big players
Big pharma craves slice of AI-based RNA drug discovery - Nature BiotechnologyIn Brief: In recent months, at least eight companies have been launched to develop RNA-modulating small molecules, and all have signed collaborations with big players
続きを読む »
 Samples from asteroid Ryugu contain one of the building blocks of RNAThe Hayabusa 2 spacecraft brought back samples from Ryugu in 2020, and an analysis of a tiny portion of those samples has revealed key ingredients for life
Samples from asteroid Ryugu contain one of the building blocks of RNAThe Hayabusa 2 spacecraft brought back samples from Ryugu in 2020, and an analysis of a tiny portion of those samples has revealed key ingredients for life
続きを読む »
 Scientists Discover RNA Component Buried in The Dust of an AsteroidA sample extracted from an asteroid far from Earth has confirmed that RNA nucleobases can be found in space rocks.
Scientists Discover RNA Component Buried in The Dust of an AsteroidA sample extracted from an asteroid far from Earth has confirmed that RNA nucleobases can be found in space rocks.
続きを読む »
 RNA compound and vitamin B3 found in samples from near-Earth asteroid | CNNOrganic molecules, including uracil and niacin, have been detected in samples collected by Japan's Hayabusa2 mission from the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu. Uracil is a component of RNA while niacin is better known as vitamin B3, a key cofactor for metabolism.
RNA compound and vitamin B3 found in samples from near-Earth asteroid | CNNOrganic molecules, including uracil and niacin, have been detected in samples collected by Japan's Hayabusa2 mission from the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu. Uracil is a component of RNA while niacin is better known as vitamin B3, a key cofactor for metabolism.
続きを読む »
 We Found the Building Blocks of Life Hiding in Asteroid DustPristine rock samples taken from asteroid Ryugu are home to uracil, a critical component of RNA.
We Found the Building Blocks of Life Hiding in Asteroid DustPristine rock samples taken from asteroid Ryugu are home to uracil, a critical component of RNA.
続きを読む »
