Engineering advance allows particles to be placed deeper within biological tissue, which could aid with cancer diagnosis or monitoring. Fluorescent sensors, which can be used to label and image a wide variety of molecules, provide a unique glimpse inside living cells. However, they typically can
MIT engineers found a way to dramatically improve the signal emitted by fluorescing nanosenors. The researchers showed they could implant sensors as deep as 5.5 centimeters in tissue and still get a strong signal. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers and edited by MIT News
According to the researchers, this type of technology might allow fluorescent sensors to be used to track specific molecules inside the brain or other tissues deep within the body, for medical diagnosis or monitoring drug effects. “All tissues autofluoresce, and this becomes a limiting factor,” Koman says. “As the signal from the sensor becomes weaker and weaker, it becomes overtaken by the tissue autofluorescence.”
One possible application for this kind of sensing is to monitor the effectiveness of chemotherapy drugs. To demonstrate this potential, the researchers focused on glioblastoma, an aggressive type of brain cancer. Patients with this type of cancer usually undergo surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, then receive the chemotherapy drug temozolomide to try to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
When temozolomide enters the body, it gets broken down into smaller compounds, including one known as AIC. The MIT team designed a sensor that could detect AIC, and showed that they could implant it as deep as 5.5 centimeters within an animal brain. They were able to read the signal from the sensor even through the animal’s skull.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
 A Groundbreaking Engine Uses Information as FuelTheir system can generate enough power that is 'comparable to molecular machinery in living cells,' with 'speeds comparable to fast-swimming bacteria.'
A Groundbreaking Engine Uses Information as FuelTheir system can generate enough power that is 'comparable to molecular machinery in living cells,' with 'speeds comparable to fast-swimming bacteria.'
続きを読む »
 MIT Engineers Devise a Recipe for Improving Any Autonomous Robotic SystemA new general-purpose optimizer can speed up the design of walking robots, self-driving vehicles, and other autonomous systems.
MIT Engineers Devise a Recipe for Improving Any Autonomous Robotic SystemA new general-purpose optimizer can speed up the design of walking robots, self-driving vehicles, and other autonomous systems.
続きを読む »
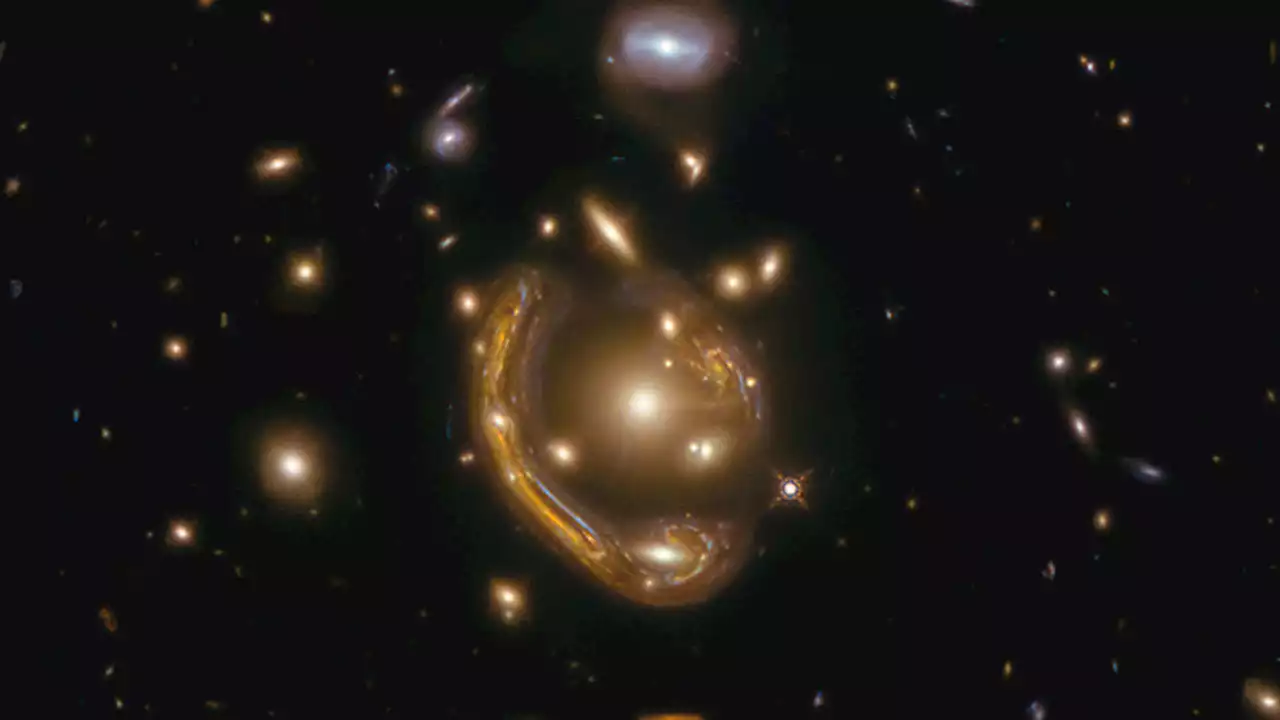 Molten 'Einstein Ring' Offers Glimpse Into a Galaxy 9.4 Billion Light-Years AwayA donut-like ring of light has allowed scientists to observe what's going on in a galaxy near the beginning of time.
Molten 'Einstein Ring' Offers Glimpse Into a Galaxy 9.4 Billion Light-Years AwayA donut-like ring of light has allowed scientists to observe what's going on in a galaxy near the beginning of time.
続きを読む »
 Sony Music, Live Nation, Netflix, More Offer Staff Travel Reimbursement for AbortionsFrom media organizations to sporting goods, companies are reassuring staff about reproductive rights care following the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade
Sony Music, Live Nation, Netflix, More Offer Staff Travel Reimbursement for AbortionsFrom media organizations to sporting goods, companies are reassuring staff about reproductive rights care following the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe v. Wade
続きを読む »
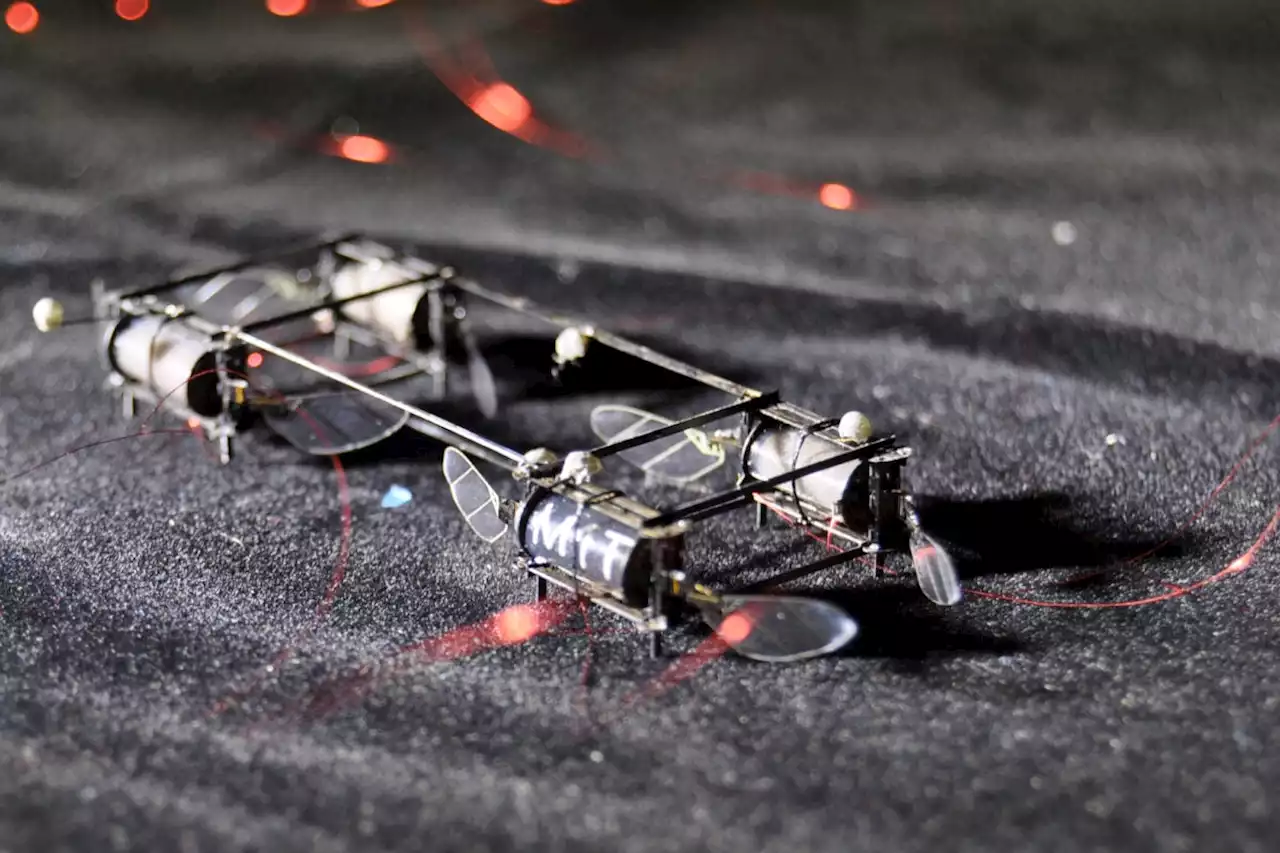 MIT engineers have created tiny robot lightning bugsEngineers gave these lightweight machines the ability to glow in the air as methods of communication and tracking.
MIT engineers have created tiny robot lightning bugsEngineers gave these lightweight machines the ability to glow in the air as methods of communication and tracking.
続きを読む »
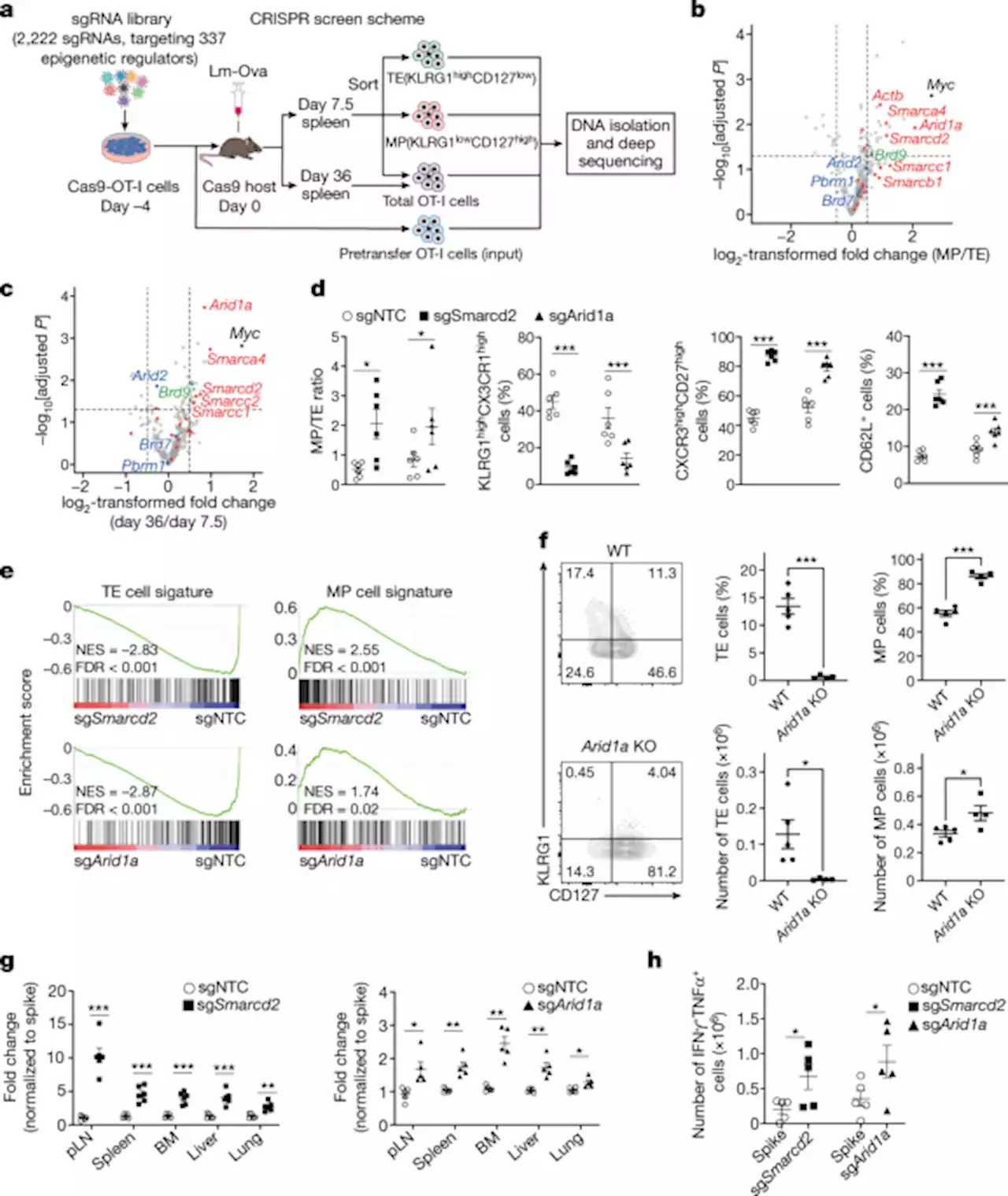 cBAF complex components and MYC cooperate early in CD8+ T cell fate - NaturecBAF is a negative determinant of memory T cell fate and the manipulation of cBAF early in T cell differentiation can improve cancer immunotherapy.
cBAF complex components and MYC cooperate early in CD8+ T cell fate - NaturecBAF is a negative determinant of memory T cell fate and the manipulation of cBAF early in T cell differentiation can improve cancer immunotherapy.
続きを読む »
