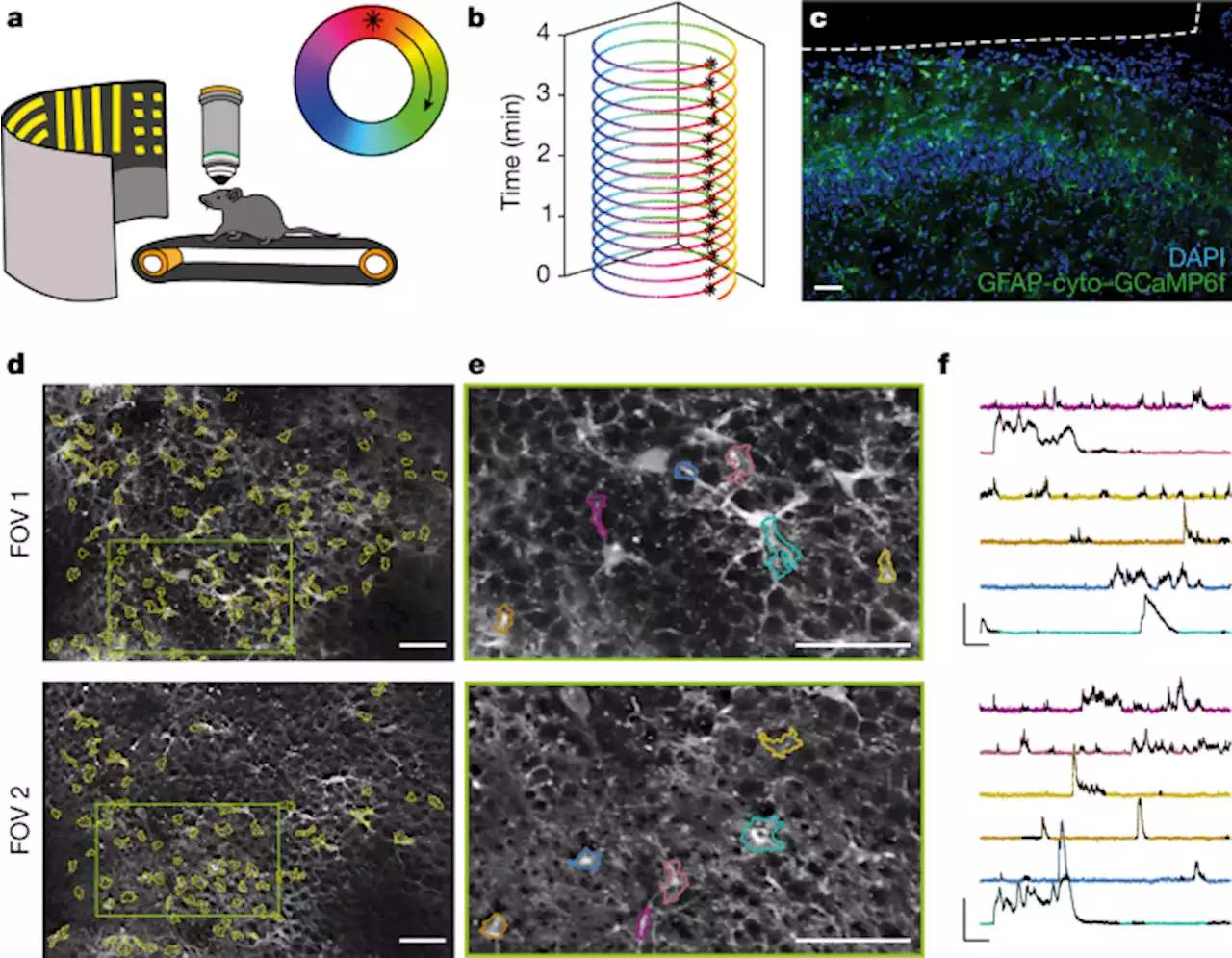
Nature research paper: Hippocampal astrocytes encode reward location
Extended Data Fig. 3 Astrocytic Activity Does Not Ramp Towards Rewarding Location in a New Environment.. The correlation between location and astrocytic activity in repeated active ROIs was significantly higher in the familiar environment compared to the new one . The repeated active ROI pairs that had significant mutual information in each environment of the mouse shown in Fig..
The mean normalized number of concurrent events as a function of location in the familiar environment and in the new environment for all active ROIs, not just the repeated ones, in the 7 mice shown in Fig.. The ramping of astrocytic activity is significantly larger in the familiar environment than in the new environment . Two mice were imaged for the third time in the familiar environment after the exposure to the new environment.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
 The Fall of Roe Finally Prompts the FTC to Protect Our Location DataThe Federal Trade Commission is suing a data broker for selling location data that could track people going to sensitive locations, like abortion clinics.
The Fall of Roe Finally Prompts the FTC to Protect Our Location DataThe Federal Trade Commission is suing a data broker for selling location data that could track people going to sensitive locations, like abortion clinics.
続きを読む »
 From the archive: pollution link to mental health, and museum envySnippets from Nature’s past.
From the archive: pollution link to mental health, and museum envySnippets from Nature’s past.
続きを読む »
Dysregulated naïve B cells and de novo autoreactivity in severe COVID-19 - NatureNature research paper: Dysregulated naïve B cells and de novo autoreactivity in severe COVID-19
続きを読む »
 The White Lotus Returns, and the Behavior Is No Better.McHenryJD visited the set of HBO's 'White Lotus' season two, which writer, director, and creator Mike White describes as “a bedroom farce with teeth'
The White Lotus Returns, and the Behavior Is No Better.McHenryJD visited the set of HBO's 'White Lotus' season two, which writer, director, and creator Mike White describes as “a bedroom farce with teeth'
続きを読む »
 Socios extends Argentina soccer deal tapping into a market ravenous for digital assetsSocios and the AFA will also build a gamified, web3-ready, engagement and rewards community for Argentine fans through the tokens, which will be built on the Chiliz blockchain.
Socios extends Argentina soccer deal tapping into a market ravenous for digital assetsSocios and the AFA will also build a gamified, web3-ready, engagement and rewards community for Argentine fans through the tokens, which will be built on the Chiliz blockchain.
続きを読む »