Gut-lung axis: Using commensal bacteria to reinforce mucosal immunity Bacteria Coronavirus Disease COVID Immunity mucosal immunology mucosalvaccines pathogens COVID gutmicrobiome epitope karolinskainst DKU2017 MDPIOpenAccess
By Dr. Liji Thomas, MDJul 19 2022Reviewed by Benedette Cuffari, M.Sc. Mucosal pathogens are responsible for many severe infectious diseases, including influenza, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronaviruses 1 and 2 , rotaviruses, and gut pathogens like Salmonella or Escherichia coli. The ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has demonstrated the urgency to develop vaccines that can induce both mucosal and systemic adaptive immunity.
The next generation of vaccines may be based on reverse vaccinology and structure-based RV to improve vaccine design using readymade vectors and formulations. Eventually, this may lead to the discovery of better vaccine targets, functional epitopes, and data on viral and vector functions. In the current review paper, the authors demonstrate how the microbial tools used to ensure homeostasis in the gut microbiome produce mucosal immunity and may lead to the development of bacterial vectors for pathogenic viruses like SARS-CoV-2 for future protective mucosal vaccines.
Since the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue mounts mucosal immune responses, the appropriate MALT must be stimulated to achieve the desired immune response. The different types of MALT tissues include gut-, nasopharynx-, and bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue that is abbreviated as GALT, NALT, and BALT, respectively.
The gamma delta T-cells are another T-cell subtype that responds to common microbial or host antigens that arise during infection, stress, or cancerous changes, in each of which the δ-chain is different. These are CD3+ cells with cytotoxic capabilities, independent of MHC binding. However, it is crucial to keep in mind the safety issues regarding the use of live-attenuated pathogenic bacteria as a recombinant delivery system due to their potential for reversion to the pathogenic state, which requires further studies.”
Several strains, including L lactis, L. casei, L. plantarum, and L. helveticus have been experimentally demonstrated to produce a robust immune response to many infections.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
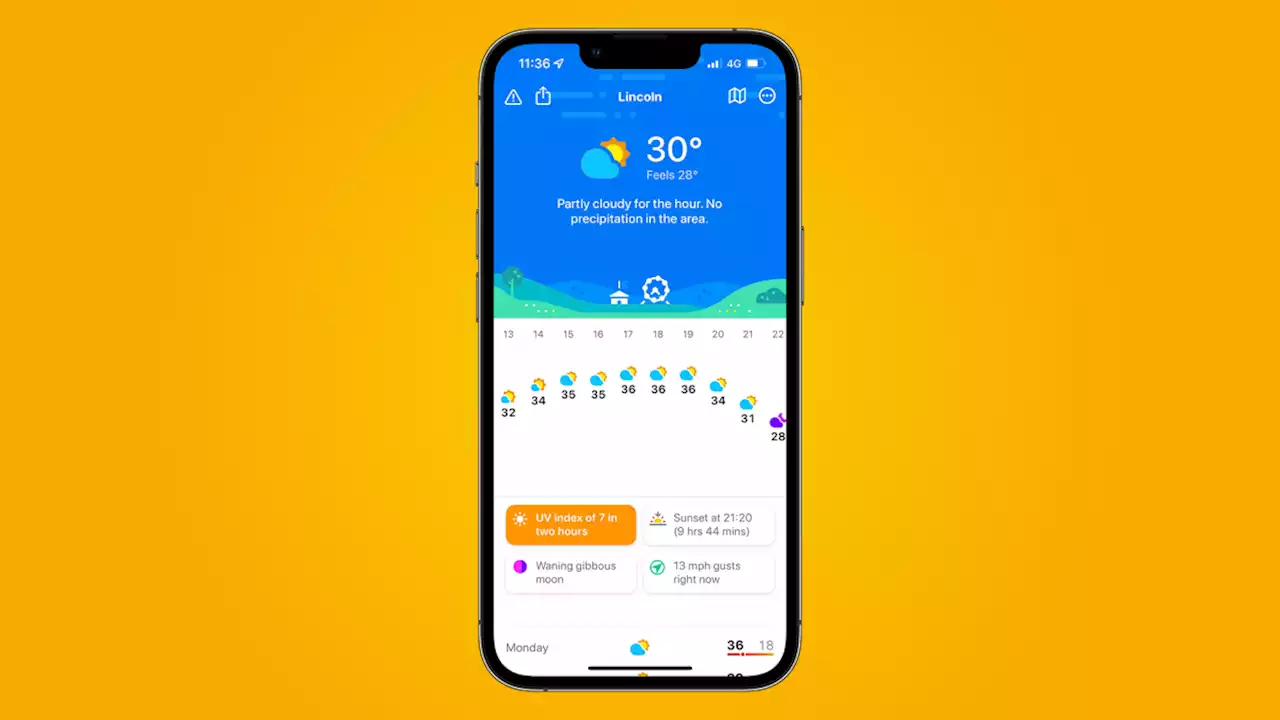 The three apps I'm using to keep me cool through the heatwaveHow I'm using these apps on my iPhone, Watch and PC to help me handle the heatwave this week.
The three apps I'm using to keep me cool through the heatwaveHow I'm using these apps on my iPhone, Watch and PC to help me handle the heatwave this week.
続きを読む »
 Researchers assess the evolution and diversity of monkeypox virus genomes using phylogenomic analysisResearchers assess the evolution and diversity of monkeypox virus genomes using phylogenomic analysis IcahnMountSinai evolution monkeypox virus genome phylogenomics virus virology
Researchers assess the evolution and diversity of monkeypox virus genomes using phylogenomic analysisResearchers assess the evolution and diversity of monkeypox virus genomes using phylogenomic analysis IcahnMountSinai evolution monkeypox virus genome phylogenomics virus virology
続きを読む »
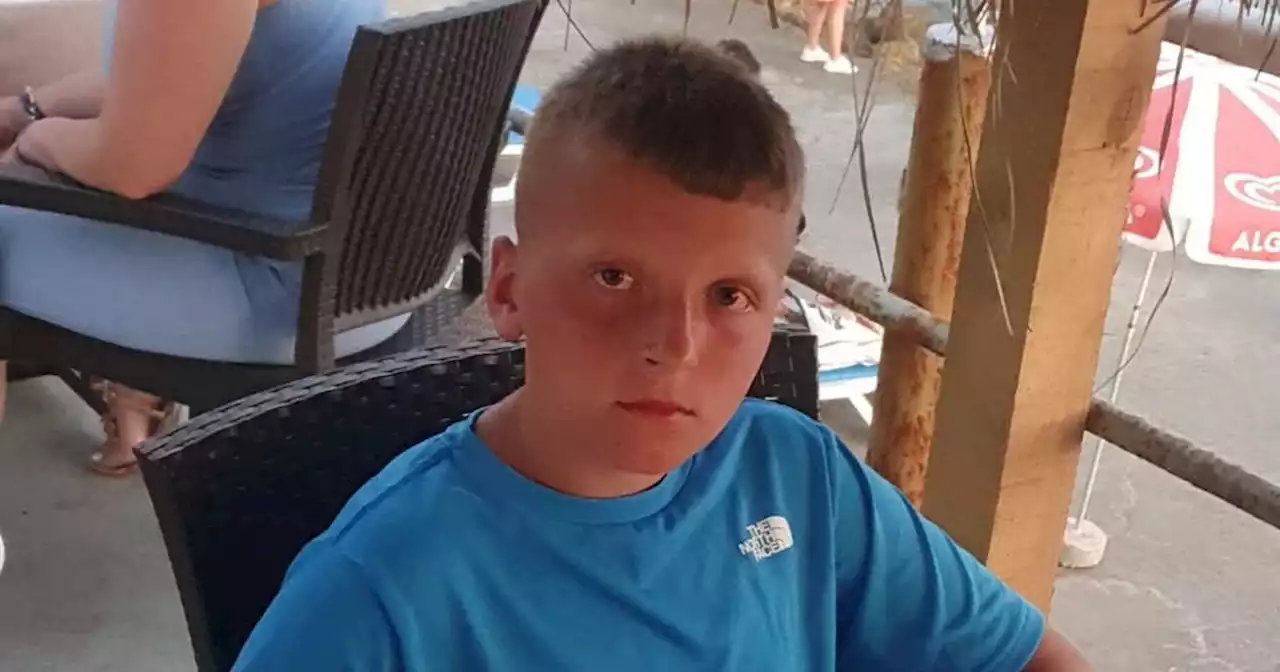 Schoolboy covered in agonising blisters despite using sun creamAwful - he did everything he thought he should, but it's 'ruined his first holiday in three years' 🙁
Schoolboy covered in agonising blisters despite using sun creamAwful - he did everything he thought he should, but it's 'ruined his first holiday in three years' 🙁
続きを読む »