With a mass of around three-quarters of our Sun crammed into a ball that could sit comfortably inside Manhattan, the compact object XMMU J173203.3-344518 is certainly remarkable.
The lightest detectedAt 77 percent of a solar mass, XMMU J173203.3-344518 isn't merely record-breaking; it's downright confusing. Neutron stars have no business being so petite.strange star
Comparing their results with strange matter equations and speculative models for their creation in supernovae, the team agreed this weird little object still has all of the hallmarks of a hypothetical strange star. Quarks happen to come in a variety of forms or flavors. 'Up' and 'down' flavors mix and match to form protons and neutrons. With sufficient pressure, down quarks can transform into up quarks, which in turn can switch into another flavor – a strange quark.
日本 最新ニュース, 日本 見出し
Similar News:他のニュース ソースから収集した、これに似たニュース記事を読むこともできます。
 Brightest Gamma-ray Burst Shines Light on Milky Way StructureBrightest Gamma-ray Burst Shines Light on Milky Way Structure - by Astroguyz
Brightest Gamma-ray Burst Shines Light on Milky Way StructureBrightest Gamma-ray Burst Shines Light on Milky Way Structure - by Astroguyz
続きを読む »
 Astronomers found a lonely galaxy that ate all its friendsAstronomers have spotted a lonely galaxy over 9 billion light-years from Earth that could change everything we know about galaxy clusters.
Astronomers found a lonely galaxy that ate all its friendsAstronomers have spotted a lonely galaxy over 9 billion light-years from Earth that could change everything we know about galaxy clusters.
続きを読む »
 Astronomers develop new AI software to sharpen photos from ground-based telescopesThe software is an adaptation of the same technology you use to improve your selfies.
Astronomers develop new AI software to sharpen photos from ground-based telescopesThe software is an adaptation of the same technology you use to improve your selfies.
続きを読む »
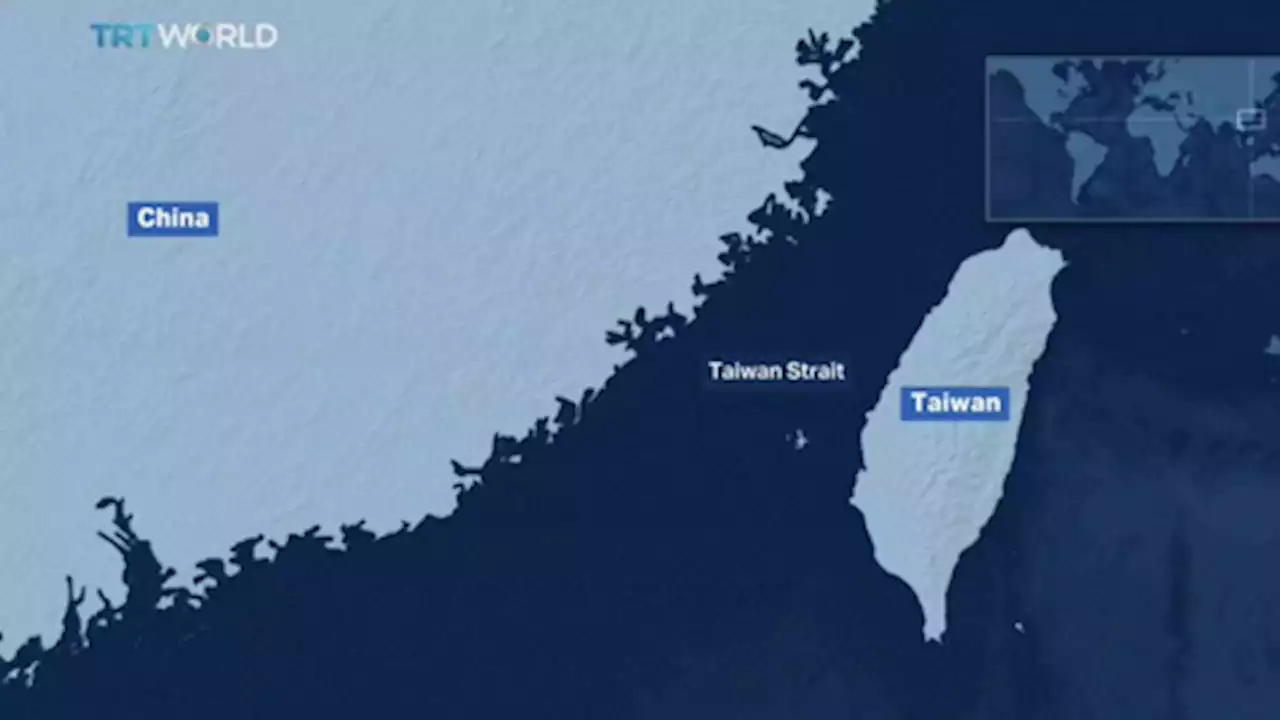 China begins new Taiwan Strait military drillsChina launches three days of military drills in Taiwan Strait, with PLA's Eastern Theatre Command saying the 'United Sharp Sword' would run for 'combat preparedness'
China begins new Taiwan Strait military drillsChina launches three days of military drills in Taiwan Strait, with PLA's Eastern Theatre Command saying the 'United Sharp Sword' would run for 'combat preparedness'
続きを読む »
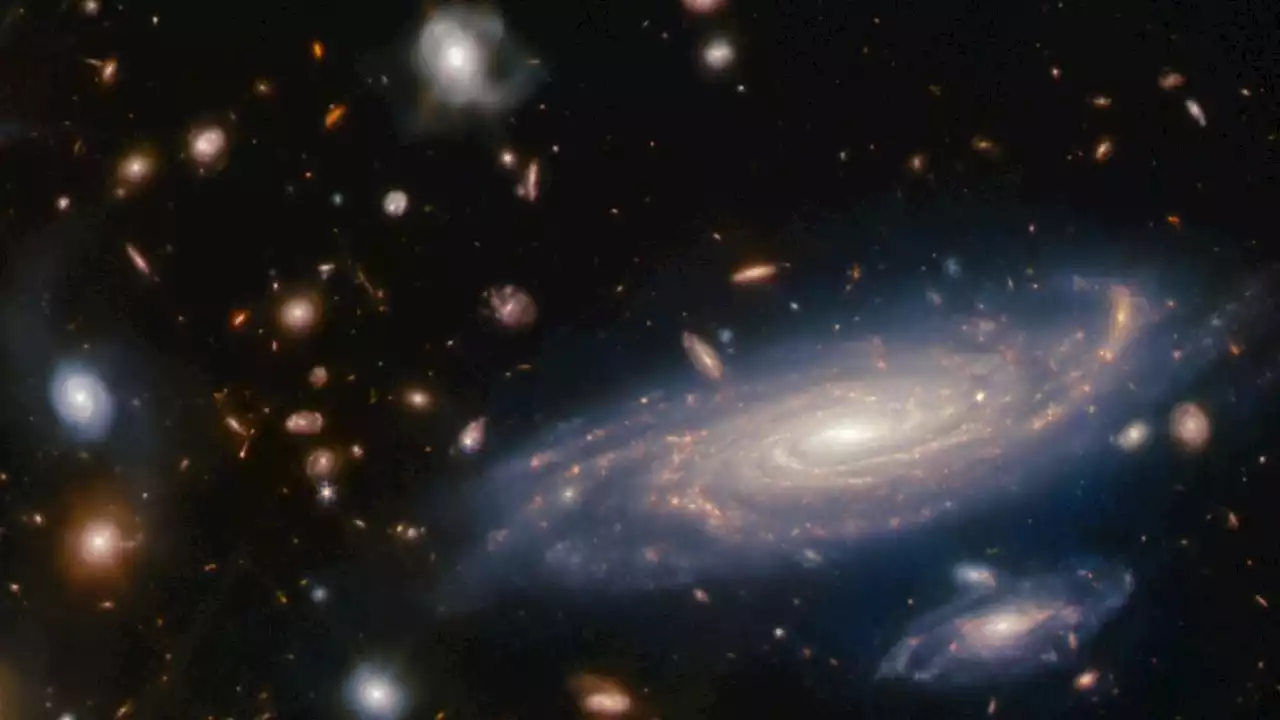 James Webb telescope discovers the 4 oldest galaxies in the universe, born just 300 million years after the Big BangAstronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have detected the four oldest galaxies in the known universe, which are forming stars much faster than thought possible.
James Webb telescope discovers the 4 oldest galaxies in the universe, born just 300 million years after the Big BangAstronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have detected the four oldest galaxies in the known universe, which are forming stars much faster than thought possible.
続きを読む »
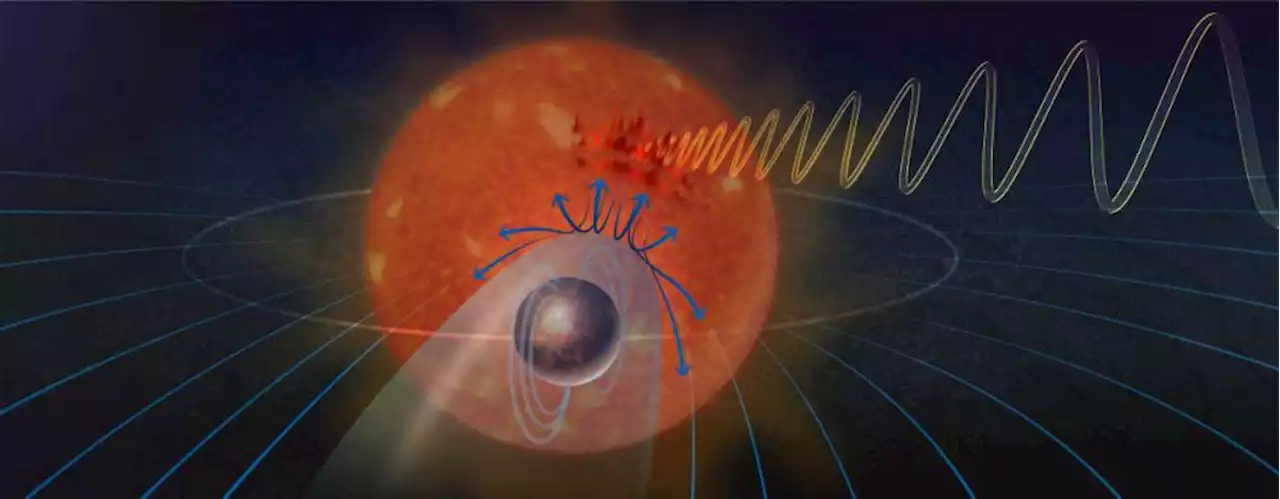 Do Repeating Radio Signals Indicate an Exoplanet with a Magnetosphere?Astronomers may have found a way to detect an exoplanetary magnetosphere using radio emissions from outbursts at the parent star.
Do Repeating Radio Signals Indicate an Exoplanet with a Magnetosphere?Astronomers may have found a way to detect an exoplanetary magnetosphere using radio emissions from outbursts at the parent star.
続きを読む »
